I recently published an article on Why Kyokushin Fighters Do Not Punch to the Face. It received a lot of feedback! Many people were favouring punching to the head, with the argument that it’s the only way to train realistically, and that Kyokushin sport fighters are ill prepared because of this.
I was shocked though that no one mentioned the absolute danger involved in striking to the head.
Concussive head trauma is real folks! It is the reason many MMA fighters have cut head strikes out of their training, and/or reduced heavy sparring dramatically. The dangers and repercussions of concussions are far to grave.
Very recently here in Canada, new rules were passed by the Canadian Football League (CFL) to eliminate contact in Football practice. Effective immediately, there will be no padded practices allowed after training camp and, by effect, much less contact. Both the Canadian and American arms of the Concussion Legacy Foundation provided statements praising the CFL’s action.
Concussions are no joke! There is extremely concerning evidence on the long-term effects of repetitive brain trauma.
CTE results in a progressive decline of memory and cognition, as well as depression, suicidal behavior, poor impulse control, aggressiveness, parkinsonism, and, eventually, dementia. In some individuals, it is associated with motor neuron disease, referred to as chronic traumatic encephalomyelopathy, which appears clinically similar to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
I personally know a high-level boxer who at a very young age has been affected by this. It is heart-breaking to watch.
What many people don’t realize is that the issue isn’t with the impact of the strike. It is the jarring of the head and the brain literally smashing against the inside of the head.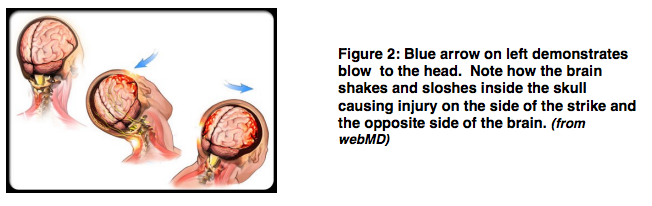
 Many people advocate for Protective Headgear, but this does very little for concussion damage. It will protect your nose, eyes and jaw, but as stated above, the issue isn’t with the impact of the strikes, it is the jarring of the head causing the brain to slosh around smashing against the inside of the skull. This is why football is instituting no padded practices, because of the false sense of security in helmets and protective clothing.
Many people advocate for Protective Headgear, but this does very little for concussion damage. It will protect your nose, eyes and jaw, but as stated above, the issue isn’t with the impact of the strikes, it is the jarring of the head causing the brain to slosh around smashing against the inside of the skull. This is why football is instituting no padded practices, because of the false sense of security in helmets and protective clothing.
There is actually a huge argument to have MMA done without gloves. Again, because of the false sense of safety. Here is an experiment you can do yourself. Punch a wall as hard as you can. Now punch it with a boxing or mma glove, even better with taped wrist. Guaranteed you will punch harder with the glove, because there is less chance of damaging your hand. This is why Rugby players have less injuries that American Football players. The American Football player feels more secure, so will hit with much more force, compared to the Rugby player.
Recently I had my own incident, when I received a jodan mawashi that caught me in the rear base of the skull. At the time I was slightly shaken, but ok. Well enough to continue sparring and do a few more rounds. However, the next day I was stomach sick, two days later a sever migraine that lasted a week, all due to the minor concussion I received. Thankfully it was minor and not a common occurrence. If however I had been receiving repetitive head strikes through face punching, that kick could have been a lot more dangerous.
Second-impact syndrome (SIS), describes the situation in which an individual sustains a second head injury before the symptoms from the first head injury have resolved. The second injury may occur from days to weeks following the first. Loss of consciousness is not a requirement of this condition, the impact may seem relatively mild, and the athlete may appear only dazed initially. However, this second impact causes cerebral edema and herniation, leading to collapse and death within minutes.
Even if you don’t receive strikes hard enough to cause such damage, the repetitive head trauma from lighter sparring can be just as bad.
Repetitive Head Injury Syndrome
Numerous studies of professional boxers have shown that repeated brain injury can lead to chronic encephalopathy, termed dementia pugilistica.1, 2, 3, 4
Before you think it won’t happen to you, consider if that’s a risk you’re willing to take. It’s one thing if you’re doing it as a career (and we’ve all seen the punch-drunk fighters), but it’s another if you’re doing this as a hobby.
And don’t be fooled by headgear. It doesn’t do anything except protect the fists and maybe your nose from being broken. It does very little to reduce concussion. If anything it might be worse, taking more blows because of the false sense of security. There is an argument that going bare-knuckle would reduce head trauma, because people would use less strikes, because of the risk of broken hands.
So, before you advocate faces trikes, remember:
The major 5 Risks of Repetitive Head Impacts:
1. Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE)
CTE is a degenerative brain disease found in athletes, military veterans and others with a history of repetitive brain trauma. In CTE, a protein called Tau forms clumps that slowly spread throughout the brain, killing the brain cells. Clinical symptoms of CTE include the progressive decline of memory and cognition, depression, suicidal behaviour, poor impulse control, aggressiveness, Parkinsonism and dementia.
Evidence suggests that CTE is caused by repetitive hits to the head sustained over a period of years. It’s important to note that you don’t have to suffer from a full-blown concussion to get this disease. In fact, evidence points to subconcussive impacts, or repetitive hits to the head as the biggest factor!
2. Depression
Depression is a mental disorder that affects how someone feels, thinks and acts. It can lead to a variety of emotional and physical problems that can decrease a person’s ability to function at work and at home. Symptoms can include a loss of interest in activities once enjoyed, changes in appetite, sleeping issues and even thoughts of death or suicide.
3. Dementia Pugilistica
Also known as “punch-drunk syndrome,” dementia pugilistica is a neurodegenerative disease found in people who have suffered multiple concussions. People who suffer from this condition commonly experience tremors, slowed movement, speech problems, confusion, a lack of coordination and memory problems.
Dementia pugilistica is a variant of CTE, and it also shares some histological features of Alzheimer’s disease at the microscopic level. While it has been identified primarily in boxers who experienced repeat impacts to the head, other athletes may also suffer from this condition. In fact, it’s possible that available data on neurodegenerative features in boxers may provide insights for understanding less severe head injuries.
4. Neurocognitive Impairments
The signs and symptoms of a concussion can often affect one’s cognitive abilities, resulting in an inability to concentrate, confusion, irritability and loss of balance. When you suffer more than one traumatic brain injury over the course of your life, you may be at greater risk of developing lasting, possibly progressive, impairment that limits function.
5. Slower Neurological Recovery
Every year, millions of people sustain concussions, but the risks of a prolonged recovery after repeat concussions still remains new territory. Nevertheless, a study suggests that history of multiple concussions may be associated with a slower recovery of neurological function after another concussion. It also suggests that repeat concussions may result in permanent neurocognitive impairment. That’s why it’s utterly important to never return to sports or dangerous activities until you have fully healed.
I love combat sports and martial arts, but not enough to throw away my life, especially as I get older. The rules of sport Kyokushin suit me just fine. I can even mix in grappling to make it more complete, but I don’t have to jeopardize my mental health to do so.
So, before you slam Kyokushin about not being realistic without face strikes, think long and hard. If you are training in such manner, what type of damage are you doing. It might not be effecting you now, or like my friend it might be… in your 30s. Or perhaps it will be in your 50s, when you are getting ready for retirement, and can’t recognize your own children. Doesn’t sound like fun for me.
If you are going to practice striking to the head, make sure you do it under VERY controlled conditions, to minimize the damage.
Even without face-punching in the sport aspect of Kyokushin, it is full-contact, bare-knuckle fighting, with a very wide variety of skills on display.
As I said in closing of the original article, for me Kyokushin is the strongest karate, not because of its great fighting ability, which I think it has, but because it has a history and reputation of indomitable sprit. The spirit of OSU! To never give up!
OSU!
- Ryan AJ. Intracranial injuries resulting from boxing. Clin Sports Med. Jan 1998;17(1):155-68. [Medline].
- Kaste M, Kuurne T, Vilkki J,. Is chronic brain damage in boxing a hazard of the past?. Lancet. Nov 27 1982;2(8309):1186-8. [Medline].
- Beaussart M, Beaussart-Boulengé L. “Experimental” study of cerebral concussion in 123 amateur boxers, by clinical examination and EEG before and immediately after fights. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. Nov 1970;29(5):530. [Medline].
- Johnson J. Organic psychosyndromes due to boxing. Br J Psychiatry. Jan 1969;115(518):45-53. [Medline].


A few years ago I would have said you guys are pussies. But after 13 years of full contact goju-ryu (throughout my 30’s) and, high school football, rugby, and about 100 street fights. Now approaching 50 years old. I would say, you are a smart man and that is smart training. Maybe an occasional night of light face contact would be good but I wish I could undo all the damage I have done to my head. Don’t think it’s macho to get hit in the head (like I used to think) It is just plain stupid. Take it from… Read more »
This is not a comment on possibilities of head trauma, but rather post-injury and Kyokushin… In early 2015, my 25 year old son was hit by a car and suffered a severe traumatic brain injury, broken hip, shattered left arm, broken ribs, and punctured lung. After9 months in hospital (4 in coma/acute care), he started in at our dojo. His team of doctors was surprised, but supportive. Our Shihan is obviously aware head strikes are forbidden with my son because a repeat, less severe TBI could have devastating consequences. Shihan does an exceptionally good job and I trust him completely… Read more »
I agree, but I am an advocate of controlled sparring to the head to elicit correct defensive fundamentals vs. punches to the face which some,but not all Kyokushin org. lack as I know some schools who do not drill facepunch drills. The rules on the street are different and people will swing at your head. When not training for knockdown tournaments, controlled facepunch sparring and drills are a must.
Notice I emphasize the word control.
Osu!
I know it is the toughest but I really admire the ultimate truth
Really kyokushin is the strongest karate in world
I think you make very good points. But since research says that even one concussions can have long-term brain damage, doesn’t what you say apply to kicks to head as well? I’ve seen some devastating head kicks in Kyokushin tournaments.
Good article and a needed one !
Thnx for the very clear and right article. As former med doctor of the Dutch Kyokushin Org. NKKO and as practising karataka I can not agree more with you. This should go all over the world.
Thank you, for this timely article. I have the same approach regarding head strikes in my Kyokushin training and I pass this to my students.